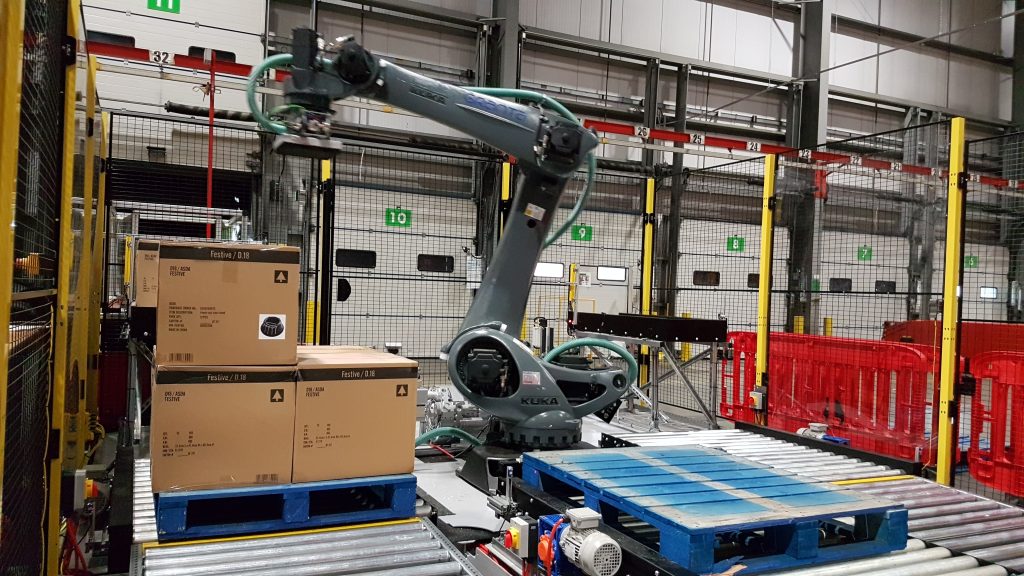
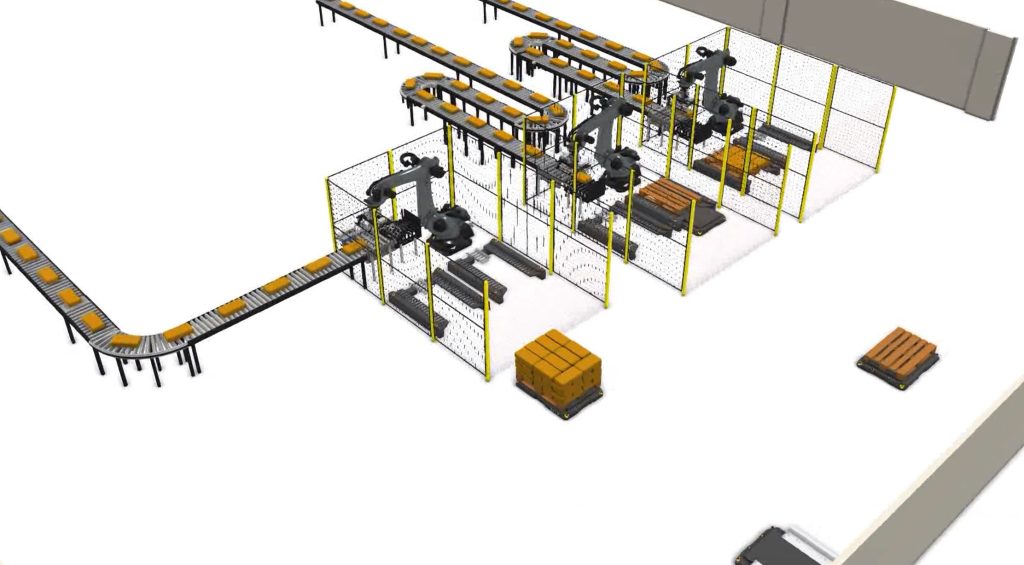
Yes, palletiser systems can work in conjunction with Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) to automate and streamline material handling and palletising processes in warehouses and manufacturing facilities. This combination of technologies can enhance efficiency, reduce labour costs, and improve overall productivity. The two key ways in which AGVs are used to work alongside palletiser systems are shown below:
- Product Delivery: AGVs can be used to transport raw materials or finished products to and from the palletiser. They can pick up products from production lines, storage areas, or other locations and deliver them to the palletiser’s loading area.
- Pallet Transport: Once the palletiser has completed the stacking process, the AGV can transport the loaded pallets to designated storage areas or shipping docks. AGVs can navigate autonomously and follow predefined routes to ensure efficient transport.
There are many benefits to using AGVs in this way, and some of these benefits are outlined below:
- Integration and Coordination: The AGVs and palletiser system can be integrated into a centralized control system, allowing for seamless coordination and communication between these machines. This integration ensures that the right products are delivered to the palletiser at the right time and that the pallets are transported to their destination without delays.
- Flexibility: AGVs can be programmed to adapt to changes in production schedules, product types, and palletising patterns. This flexibility is valuable in environments where there is a need for frequent product changeovers or varying pallet configurations.
- Safety: Safety features such as sensors, cameras, and collision avoidance systems are incorporated into AGVs to ensure safe interaction with the palletiser and other equipment, as well as to protect workers in the vicinity.
- Efficiency and Labour Savings: The combination of AGVs and palletiser systems can significantly reduce the need for manual labour in material handling and palletising tasks, leading to cost savings and increased operational efficiency. They also reduce the need for multiple conveyors to transport product, thus creating further cost and space savings.
Overall, the integration of palletiser systems with AGVs is part of the broader trend toward automation and Industry 4.0 principles in manufacturing and logistics. This combination allows for smoother and more efficient operations, reduces the risk of errors, and enables businesses to adapt to changing demands more effectively.
If you would like to discuss your specific application in more detail, please contact us on 01223 499488 or helpline@granta-automation.co.uk.
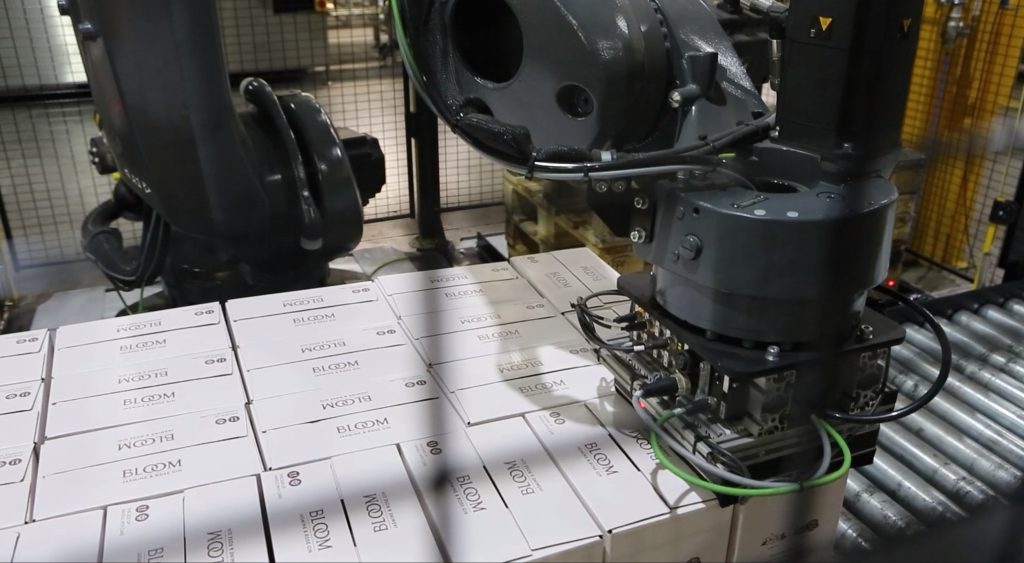





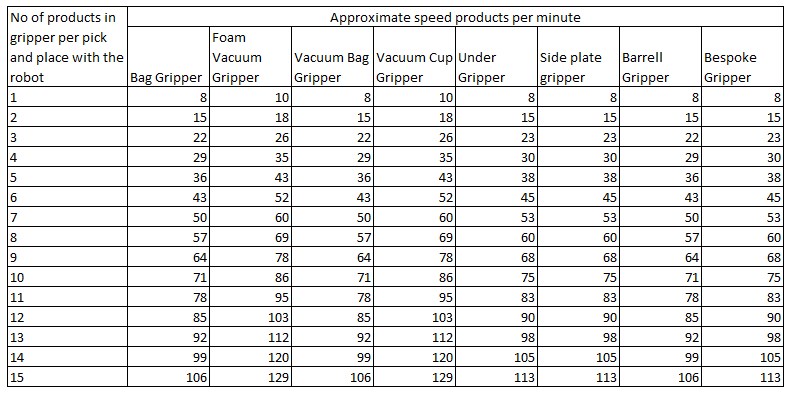




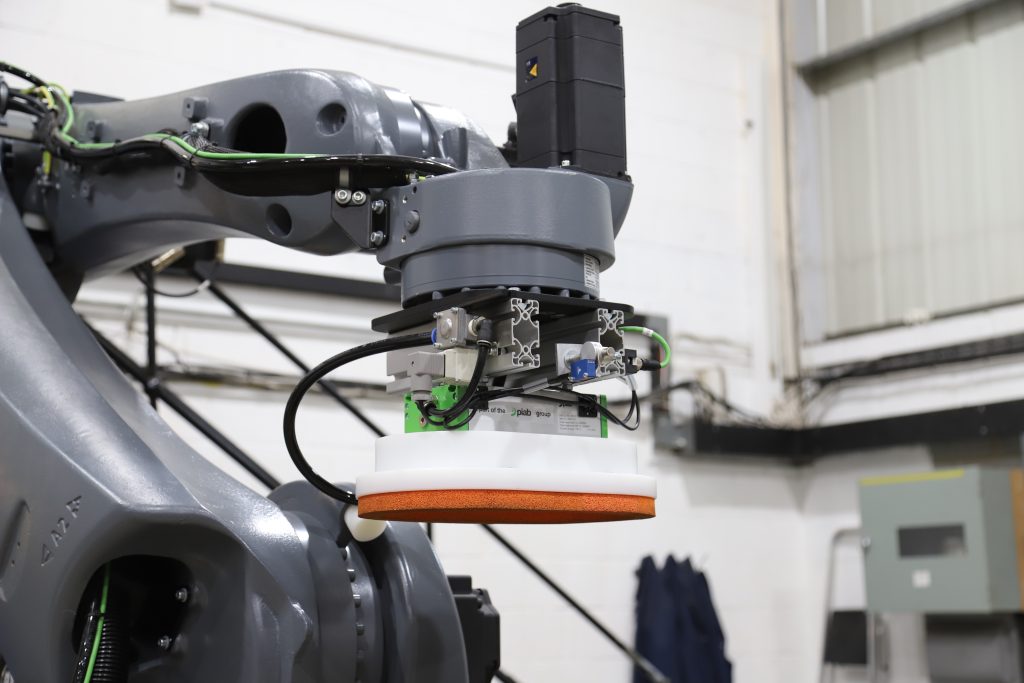
 Vacuum Bag Gripper
Vacuum Bag Gripper Vacuum Box Gripper
Vacuum Box Gripper
