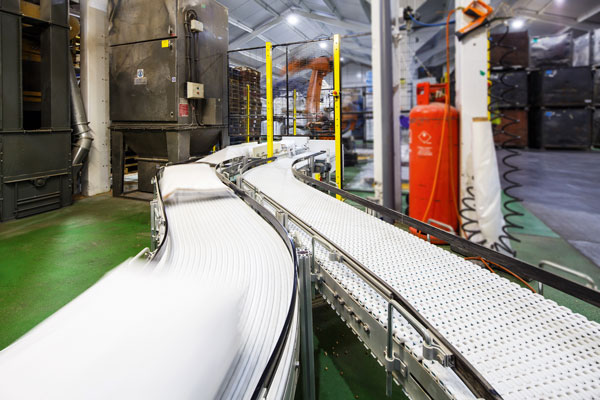
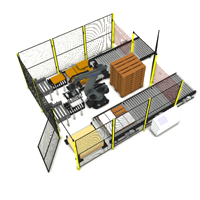
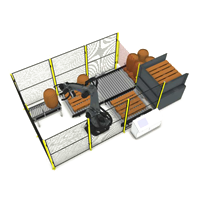
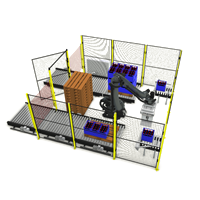
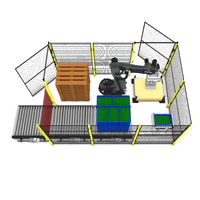
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing and distribution environments, efficiency isn’t just about speed—it’s about consistency, safety, and reliability. And nowhere is this more evident than in the palletising process. At first glance, stacking pallets might seem like a simple, low-impact task. But in reality, it plays a crucial role in safeguarding product quality, protecting your bottom line, and keeping your operations running smoothly.
This is where robotic palletisers come into their own. With the ongoing labour challenges across the industry, the increasing cost of product damage during transit, and the ever-growing pressure to improve health and safety, more companies are choosing to automate their palletising process. In this article, we’ll explore why robotic palletisers are becoming a must-have investment for manufacturers of all sizes—and how they can transform the way you stack.
Manual Palletising: Small Errors, Big Costs
Manual pallet stacking is a labour-intensive process that relies heavily on individual attention to detail, physical stamina, and on-the-spot decision-making. Unfortunately, even the most experienced operatives can make mistakes—particularly when under time pressure or dealing with repetitive tasks over long shifts.
The most common issues caused by manual stacking include:
- Inconsistent stack height and alignment, leading to unstable pallets.
- Overhanging product, which not only risks damage but also wastes valuable pallet and lorry space.
- Human error, such as missed boxes, improper stacking sequences, or improper wrapping.
These issues might seem minor on an isolated basis, but when scaled up across hundreds or thousands of pallets a week, the cost can be significant. Not only can it result in product returns and wasted materials, but it can also create delays in shipping, increase customer complaints, and lead to potential health and safety breaches on the shop floor.
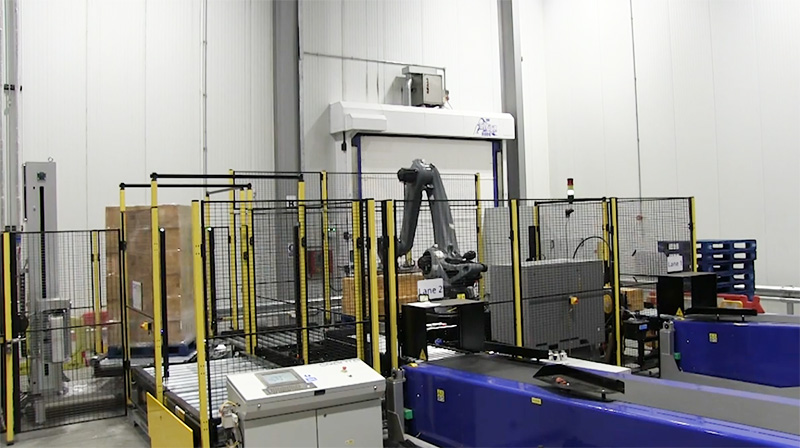
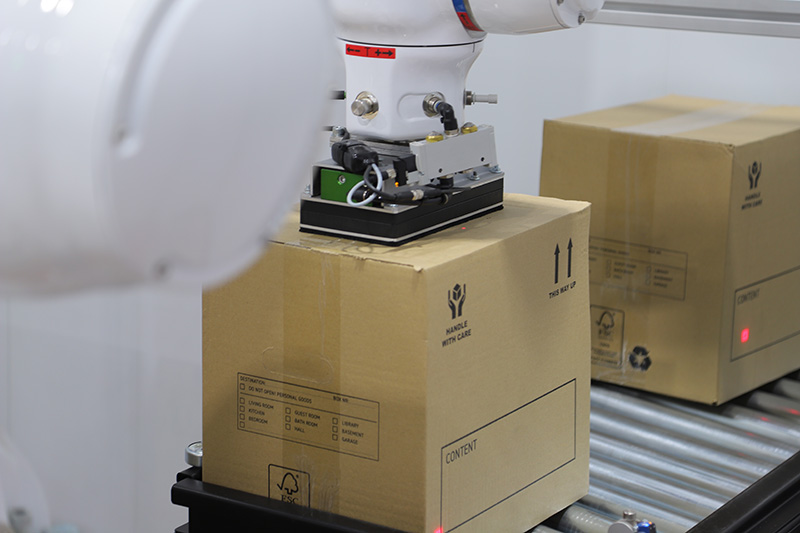
Robotic Palletisers: Built for Precision and Performance
Unlike manual operators, robotic palletisers don’t suffer from fatigue, distraction, or inconsistency. They follow programmed patterns with millimetre precision—every pallet, every time. This repeatability is where the true value of automation lies.
With a robotic palletising system, you benefit from:
- Perfectly aligned, stable stacks, reducing the risk of tipping or collapse.
- Optimised pallet configurations, using space more efficiently and fitting more product per load.
- High-speed performance, significantly increasing throughput without compromising quality.
Advanced systems also allow for flexible pallet patterns, meaning the robot can handle different products, packaging types, and stack formats with ease. Whether you’re stacking heavy cartons, shrink-wrapped trays, or awkwardly shaped boxes, a robotic palletiser can be programmed to adapt.
The Link Between Stack Quality and Product Returns
Many manufacturers don’t realise how closely product returns are linked to palletising quality. Damaged goods often occur after they’ve left your facility—due to shifting during transit, poor support, or crushed packaging from unstable stacking. Every return represents lost time, additional handling costs, and potential loss of future business.
Robotic palletisers dramatically reduce these issues by ensuring every pallet is stacked to the exact same high standard. Products arrive in perfect condition, customers receive what they expect, and your reputation for quality remains intact.
In some industries, this consistency can also help meet customer compliance standards or transport regulations. For example, food, pharmaceutical, or retail sectors often require uniform pallet loads for automated warehousing systems or store deliveries. Robotic palletising helps ensure these requirements are met—every time.
A Smarter Investment for Long-Term Gains
While the upfront cost of a robotic palletiser can be a concern for some businesses, the long-term financial benefits are compelling. Over time, most companies find the investment pays for itself through a combination of labour savings, reduced waste, lower return rates, and increased productivity.
Here’s how the savings stack up:
- Reduced Labour Costs: A single robotic palletiser can do the work of multiple manual operators, freeing staff for higher-value tasks elsewhere in the facility.
- Lower Product Damage: Consistent, stable stacking greatly reduces product losses in the warehouse and in transit.
- Improved Throughput: Robotic systems maintain high speeds and continuous output, helping meet rising customer demand without increasing headcount.
- Health & Safety Improvements: Automation reduces repetitive strain injuries and lowers the risk of accidents related to heavy lifting and poor stacking.
- Scalability and Flexibility: As your production grows or product lines change, robotic palletisers can be easily reprogrammed to handle new tasks.
In many cases, grants or capital allowances can also help offset the initial investment—particularly where automation improves efficiency and reduces waste. Or palletisers can be hired or purchased on a leasing scheme to remove the need for capital outlay.
Is Now the Right Time to Automate?
If your business is experiencing growing volumes, labour shortages, or high return rates due to product damage, then now could be the perfect time to consider automation. Robotic palletisers aren’t just a solution for large-scale manufacturers—they can be tailored to suit operations of all sizes and complexities.
Whether you’re looking to improve stack quality, free up staff time, or future-proof your production line, robotic palletising offers a clear return on investment.
Find Out More
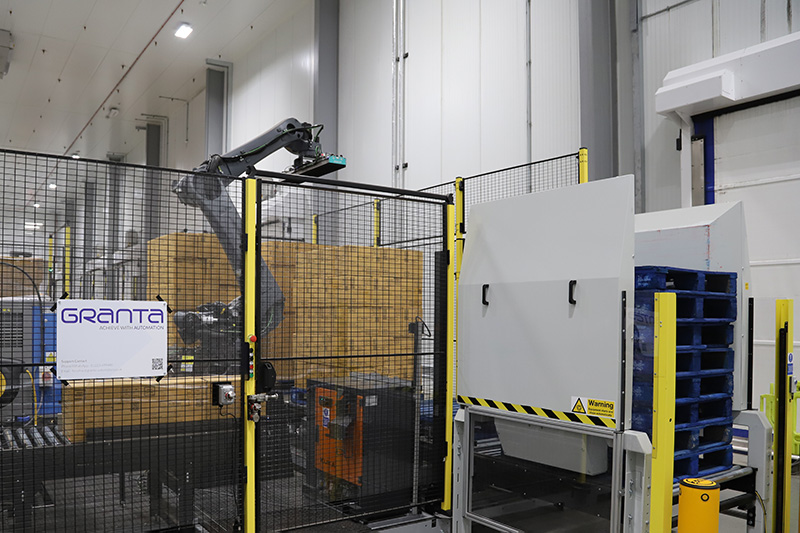
At Granta Automation, we specialise in designing and installing fully automated palletising systems that are tailored to your specific needs. Our systems integrate seamlessly with your existing processes, and our expert team can help you identify the most cost-effective way to implement automation on your line.
To learn more or to arrange a free on site assessment, get in touch with us today on 01223 499488 or contact us at helpline@granta-automation.co.uk. We will be very happy to help.
Find out more…
- The Hidden Costs of Downtime in Food & Beverage Production
- How Robotic Palletisers Deliver Fast ROI for Manufacturers
- How to Overcome Labour Shortages in Manufacturing & Logistics
- Optimising Food Production with Automated Palletising Solutions
- The Real Cost of Manual Palletising: Why Automation is the Smarter Choice