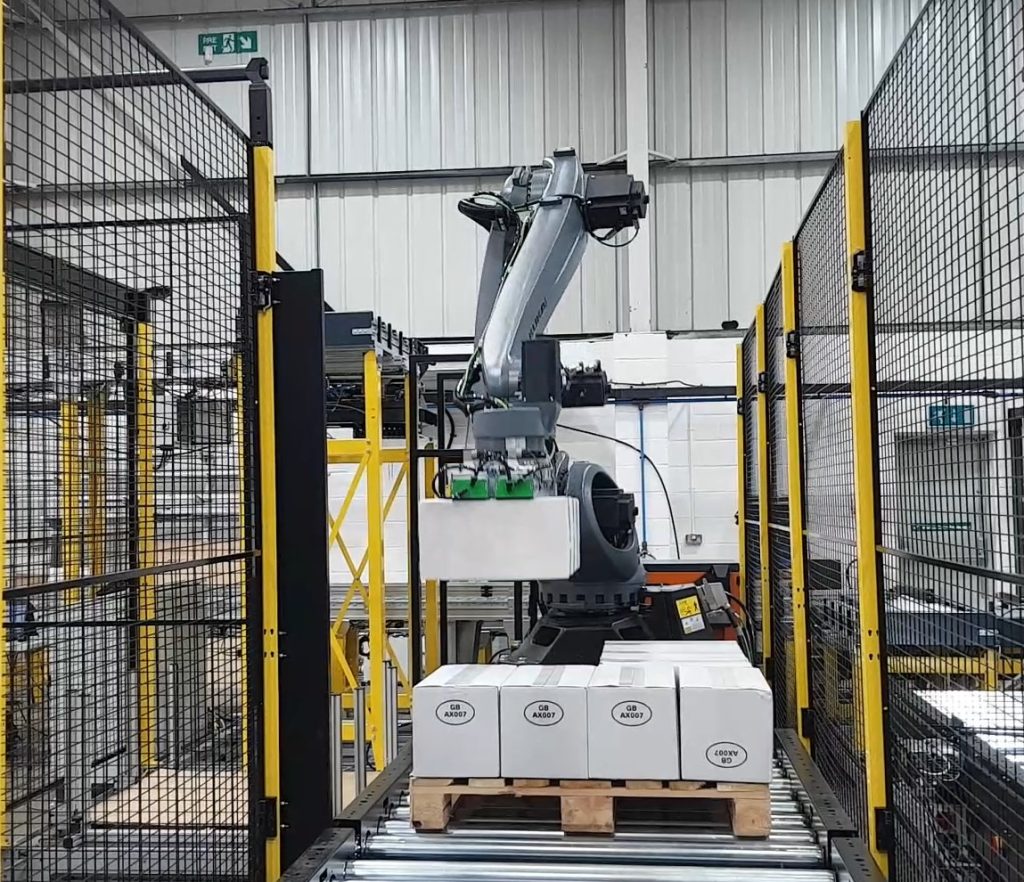
Robotic automation has long been associated with high-tech industries and multinational production lines, but in recent years, it has become increasingly accessible—and necessary—for manufacturers of all sizes. As supply chain pressures mount, labour shortages deepen, and demand for consistent, high-quality output grows, robotic automation is moving from an aspirational ideal to an operational imperative.
Yet with all its promise, automation is not without its challenges. Business leaders must consider more than just the technical feasibility. The decision to automate affects workflows, workforce planning, capital allocation, and long-term business strategy. And while the benefits can be significant, they’re not guaranteed without thoughtful planning and proper execution.
This guide explores the core advantages and disadvantages of robotic automation, helping manufacturers assess how, when, and where to deploy it for the greatest strategic gain.
Why Robotic Automation Is Gaining Ground in UK Manufacturing
The manufacturing landscape has shifted dramatically in the last decade. Rising energy costs, increasing customer expectations, and a shrinking pool of skilled workers have forced manufacturers to look inward for efficiency gains. Automation—especially robotic automation—offers a tangible way forward.
Modern robotic systems have evolved well beyond the fixed, hard-coded machines of the past. Today’s systems are intelligent, adaptable, and capable of integrating into existing production environments with minimal disruption. From high-speed pick-and-place arms to collaborative robots (cobots) that work safely alongside human operators, robotic automation offers a level of flexibility and scalability that suits a wide range of applications.
For most manufacturers, the question is no longer “Should we automate?” but rather “How do we automate in a way that makes the most sense for our business?”
Advantages of Robotic Automation
1. Enhanced Product Consistency and Repeatability
At the heart of robotic automation is one major promise: consistent output, regardless of volume or complexity. Robots follow precise programming and execute tasks identically every time. This eliminates human error and variation, especially in repetitive tasks such as assembly, cutting, sorting, and welding.
For sectors where quality control is critical—such as automotive, food and beverage, or electronics—this consistency significantly reduces waste, rework, and customer complaints. It also makes meeting ISO standards and traceability requirements much more straightforward.
2. Substantial Gains in Throughput and Productivity
Robots don’t require breaks, shift changes, or holidays. They can operate 24 hours a day, seven days a week, which allows manufacturers to scale production without a proportional increase in labour. When programmed and maintained correctly, robotic systems can dramatically increase cycle times, streamline bottlenecks, and support lean manufacturing principles.
In many cases, production lines that integrate automation experience a marked improvement in OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness), particularly through reductions in idle time and unplanned stoppages.
3. Safer, More Compliant Work Environments
Manual handling injuries, repetitive strain issues, and exposure to hazardous materials are perennial challenges in manufacturing. Robotic automation mitigates these risks by taking over the most dangerous or physically demanding tasks. From palletising heavy loads to handling high-temperature materials, robots can be deployed in ways that protect human health while ensuring compliance with health and safety regulations.
This isn’t just good ethics—it’s good business. Reducing accidents means fewer absences, fewer claims, and fewer regulatory headaches.
4. Flexibility to Scale and Adapt
Modern robotic systems are highly adaptable. Some are built with accessibility in mind, meaning they can be reprogrammed or reconfigured by production staff as production needs change. Movable robotic systems are also not on the market, allowing robotic systems to be transferred between production lines as the demand requires. This allows manufacturers to adapt quickly to new product lines, seasonal surges, or changes in demand—without having to start from scratch.
In a world where customer expectations increasingly demand agility and product customisation, this kind of operational flexibility can be a significant competitive advantage.
5. Workforce Upskilling and Strategic Deployment
One of the common misconceptions around automation is that it simply eliminates jobs. In reality, it often transforms them. When robots take on repetitive or low-skill tasks, human workers can be redeployed into higher-value roles—such as robot programming, quality control, data analysis, or system supervision.
With the right training and transition planning, robotic automation can become a platform for workforce development, rather than workforce reduction.
6. Long-Term Cost Efficiency
While automation involves a notable upfront investment, the long-term savings are substantial. Labour costs, waste, downtime, and quality defects are all reduced. Robots don’t require overtime pay, pensions, or recruitment efforts. They’re also not subject to fatigue or variation in output.
With typical ROI timeframes ranging from 12 to 36 months, depending on application, many manufacturers find that the financial justification for automation becomes stronger each year—especially in high-throughput environments or where margins are tight.
Disadvantages and Challenges of Robotic Automation
1. High Initial Capital Investment
There’s no avoiding it: robotic systems represent a significant capital outlay. From the cost of the equipment itself to integration, programming, safety guarding, and operator training, the total project budget can add up quickly. For smaller manufacturers or those operating with narrow margins, this can make automation seem out of reach—at least in the short term.
However, it’s essential to view this cost in context. Consider not just the price tag, but the long-term value created in terms of output, consistency, and scalability. Grant funding, leasing options, and hire options can also help reduce the barrier to entry and can often result in solutions that cost less than the pay back per month.
2. Integration Complexity
Retrofitting a robotic system into an existing production line isn’t always straightforward. Space constraints, legacy machinery, inconsistent upstream processes, and limited digital infrastructure can complicate the integration process. Planning is crucial.
Poor integration can negate the benefits of automation by creating new bottlenecks or causing compatibility issues. That’s why working with an experienced automation partner—who understands the full production lifecycle—is vital to achieving the right outcome.
3. Technical Skill Requirements and Change Management
Automated systems require new competencies—from programming and diagnostics to maintenance and data interpretation. Without investing in upskilling or hiring new talent, companies risk becoming dependent on external service providers, increasing downtime when issues arise. The key way to avoid this is to ensure any system you bring into your business has easy programming that anyone can use without advanced training.
Just as importantly, introducing robots into a previously manual environment requires careful change management. Staff may worry about job security or feel uncomfortable with new processes. Engaging the workforce early, providing reassurance, and offering training are all essential for a smooth transition.
4. Maintenance and Downtime Risks
Although robotic systems are highly reliable, they are not maintenance-free. Preventive maintenance schedules must be followed diligently to avoid unscheduled downtime. Replacement parts, diagnostic tools, and service support must all be considered as part of the total cost of ownership.
Without the right maintenance strategy, even a well-integrated robotic system can become a point of failure in an otherwise efficient production line.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Robotic automation is a strategic investment that demands alignment with your business model, operational challenges, and growth plans.
Ask the right questions:
- Where are your current process inefficiencies?
- What tasks are repetitive, hazardous, or prone to error?
- How much downtime or waste do you experience—and at what cost?
- Do you have the in-house capabilities to manage automation, or do you need a partner?
Robotic automation is at its most powerful when it solves a clear problem and unlocks measurable value. It’s not about automation for its own sake—it’s about making your operation more efficient, more resilient, and more competitive.
How Granta Automation Supports Manufacturers
At Granta Automation, we specialise in building robotic palletising systems that are designed to deliver results. Whether you’re looking to automate a single process, or you need a fully integrated production solution, we provide tailored, turnkey systems backed by real-world expertise.
Our approach starts with a conversation. We work with you to identify automation opportunities, quantify ROI, and design systems that suit your environment, not the other way around. From proof of concept through to installation, training, and ongoing support with very easy programming software, we’re with you every step of the way.
Ready to explore how robotic automation could transform your production line?
Get in touch with us today for a no-obligation consultation on 01223 499488 or helpline@granta-automation.co.uk, and discover how automated palletising can revolutionise your production line.
Find out more…
- Grantas Portable Cobot Palletising System: High-Performance Automation That Moves With You
- Manual vs. Automatic Palletising: A Comprehensive Comparison
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Why Every Second (and Every Pound) Counts
- The Hidden Costs of Downtime in Food & Beverage Production
- How Robotic Palletisers Deliver Fast ROI for Manufacturers